Metal stamping is a kind of manufacturing technology that can process metal sheets into precision components efficiently through die and press. The core lies in using metal stamps to apply pressure to the stamping metal, resulting in stampings products that meet the design requirements. The process has the advantages of high precision, high efficiency and low cost, and has become one of the core technologies of modern industrial manufacturing. No matter the complex geometry or micrometer level tolerance requirements, metal stamping can be produced stably by automatic production line to meet the delivery demand of many orders. JS company's high-precision molds and intelligent equipment, further improves the reliability of stamping process, helps customers shorten product development cycles, and achieves cost-saving efficiency.
What is metal stamping?
Metal stamping is an efficient manufacturing process of sheet metal into metal stampings through the synergy of metal stamp and press machines. The core principle is to use the precision structure of the die to exert high pressure on the metal plate, complete the stamping, bending, stretching and so on, and finally form a complex metal part shape. The technology is widely used in automobile parts, electronic product casings, household appliance components and so on. Metal stamping can be produced stably through automated production lines to meet the different needs of different industries.
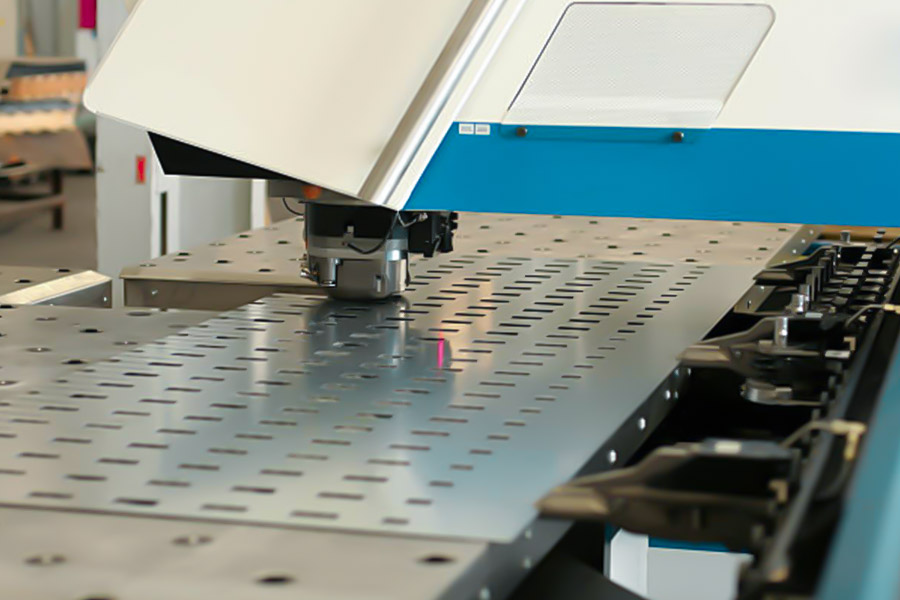

How to stamping metal?
Stamping metal is a manufacturing process in which metal sheets are processed into a specific shape through a combination of molds and presses. Here are the core steps:
1.Design and mold preparation
- According to the requirements of the parts, 3D model is designed, CAD software is used to optimize the structure, and then high-precision stamp metal molds is manufactured. Die tolerances should be controlled to ±0.01mm to ensure stamping accuracy.
- The JS team performs 3D simulation analysis of drawings uploaded by customers to optimize stamping feasibility and provide feedback on modification suggestions.
2.Material selection and pretreatment
- Common metal materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, copper, etc. should be selected according to the use of the product thickness and strength. Pre treatment includes cleaning surface oil stains and smoothing sheets to avoid cracks or deformation during stamping.
- JS can handle more than 50 materials to meet the needs of different customer and industry scenarios.
3.Execution of stamping process
- Press the sheet metal into the die and press through the press to complete the stamping, bending and stretching process in sequence. The process can produce intricately shaped metal stamped components hundreds of times a minute at a time.
- JS company uses CNC machining technology to manufacture high-precision stamping molds with a stamping cycle of up to 1 million, reducing the cost of subsequent maintenance. Automated processing lines reduce processing time by 70% and achieve rapid production within the delivery cycle.
4.Reprocessing and quality control
- After stamping, burrs need to be removed, surfaces polished and dimensions checked (e.g. coordinate measurements). Key parameters include tolerance consistency, surface roughness (Ra ≤0.8 μm), and hardness testing to ensure metal stamped finished product meet standards.
- JS offers more than 50 surface treatments and more than 20 treatment options to ensure optimal performance for all components.
5.Application and Optimization
Stamped metal is widely used in automobile parts and electronic components. By optimizing mold design or adjusting pressure parameters, production efficiency can be improved, material waste can be reduced, and the need for mass production can be met.
How to choose metal stamping molds?
Core Considerations for Selection of metal stamping molds
1.mold materials performance
The material of metal stamper directly affects the service life and machining accuracy of stamper. Carbide (e.g. tungsten steel) is suitable for stamping high hardness materials and tool steels (e.g. Cr12MoV) is suitable for medium to low strength metals. Matching materials should be selected according to the hardness and ductility of the processed metal.
2.Stamping process requirements
The process type of stamping on metal (such as stamping, stretching, bending) determines the mold structure. Complex molds require progressive molds or multi-position molds, while simple parts can be selected from a single process molds.
3.Production batch and cost balances
High-cost, long-life molds (such as cemented carbide molds) are preferred for mass production, while tool steel molds molds with better value for money are available for small production.
4.Mold accuracy and tolerance control
Precision components (e.g. electronic components) require the selection of modules ≤ ±0.01mm, whereas tolerance for ordinary structural components may be relaxed to ±0.05mm.
5.Supplier technical support
JS company has reverse engineering capabilities,such as 3D scanning to repair molds, to ensure rapid iteration and maintenance.
Metal stamping mold comparison table
| Consideration factors | Hard alloy mold | Tool steel mold | Polymer material mold |
| Applicable materials | High-hardness metals such as stainless steel and titanium alloys. | Low to medium strength metals such as aluminium and copper. | Thin aluminum sheet, plastic composite panels. |
| Life cycle (number of stamping cycles) | 1,000,000+times. | 500,000-800,000 times. | Within 100,000 times. |
| Cost | High (high material and processing costs). | Medium | Low |
| Processing accuracy | ±0.005mm (for precision components). | ±0.01mm | ±0.1mm |
| Applicable scenarios | Automotive engine components, precision connectors. | Household appliance shells, heat sink. | Small ornaments, temporary samples. |
Choose Suggestions
- High precision requirements: Priority should be given to hard alloy molds, combined with five axis machining technology to ensure detail accuracy.
- Cost sensitive project: Balance performance and budget of tool steel molds, suitable for small and medium-sized production.
- Quick verification: Polymer material molds can be used for prototype testing, shortening the development cycle.
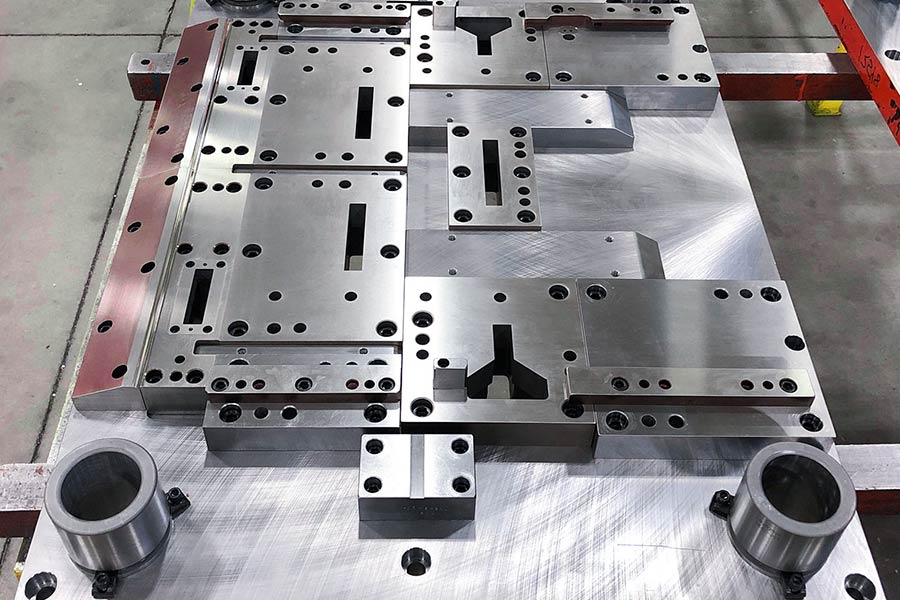

How to arrange the sequence of metal stamping process?
Metal stamping process needs reasonable arrangement according to the shape, material characteristics and precision of parts. Here is a typical process:
1.Basic process sequence
Cutting
- Purpose: Separation metal sheets to obtain initial blank or contour.
- Operations: Compatibility is controlled to ±0.1mm using cutting metallic stamp (e.g. droping die or punch die) to cut material.
- Key points: The gap between molds needs to match the thickness of the material (for example, the gap between 0.5mm aluminium plates is equivalent to about 8% thickness).
Bending
- Objective: To form a specific curvature or curvature angle through angle forming of the metallic stamp.
- Operations: Adopt V-groove mold to adjust punch stroke to prevent rebound (if stainless steel needs to be preinstalled 0.5° degree compensation).
Drawing
- Purpose: To transform a plane into a three-dimensional shape (e.g. cup and box components) using a deep pull metal stamp.
- Operations: Stretching step by step to avoid cracking and reduce friction coefficient of lubricating oil (such as mineral oil).
Forming
- Purpose: To realize complex structure such as flap and shutter by multiple metal stamps.
- Operations: Continuous die stamping reduces positioning errors and improve efficiency by more than 30%.
Finishing
- Purpose: To improve the quality of finished products by finishing metal stamps or surface molds.
- Operation: Hair removal, polishing or plating to ensure surface roughness ≤1.6μm.
2.Time to insert special process
- Hot stamping: For high-strength steel, it must be heated to more than 800 °C before being stretched and used with a high-temperature resistant metallic stamp.
- Tapping/riveting: Embedding thread or riveting in the finishing stage requires synchronous processing with a specialized composite die.
3.Principles of process arrangement
- Material utilization rate: Punch holes and cut edges to reduce waste generation.
- Deformation control: Stretch before bending to avoid rebound affecting accuracy.
- Mold lifespan: In the later stages of mold production, high wear process (such as deep stretching) is planned to reduce the wear cost of the mold.
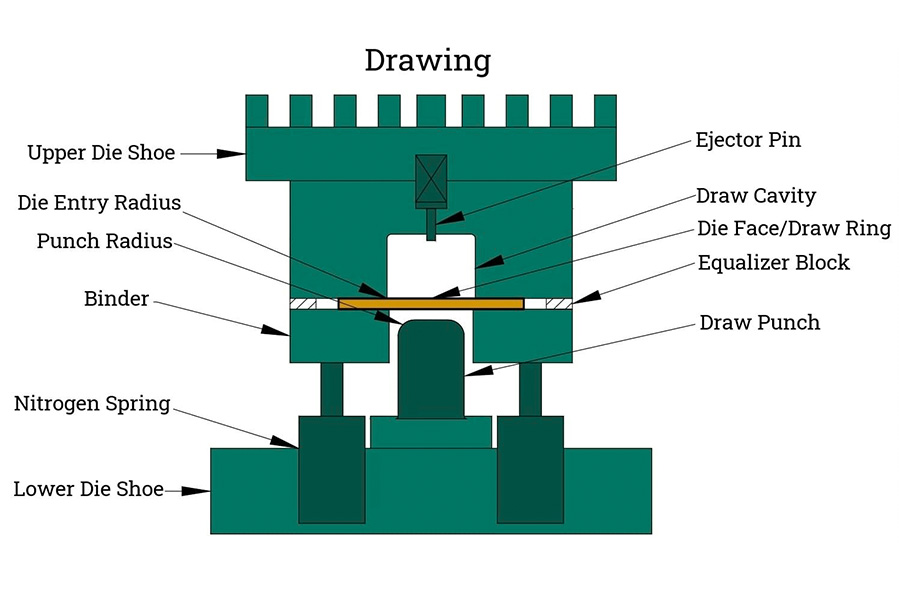
What are the effects of material hardness on metal stamping?
Main Effect of Material Hardness on metal stamping
1.Mould wear rate
- High-hardness stamping metal (such as stainless steel and titanium alloys) accelerate mold wear, resulting in increased surface roughness (Ra value 0.5-1.0 μm).
- Alloy molds (such as tungsten steel) or surface coating techniques (such as TiN coating) are needed to extend service life.
2.Adjustment of stamping process parameters
- Harder materials require greater punching force (increasing the tonnage of the press by 20% to 30%) and lower punching speed to minimize the impact loss of the die.
- Low hardness materials (such as aluminum foil) is easy to wrinkle, need to adjust the edge pressure to increase the use of lubricating oil.
3.Quality of finished products and tolerance control
- When the hardness of stamping metal is greater than HRC 45, the tensile forming limit decreases decreases, cracks are easy to appear, and progressive stamping and additional annealing processes required.
- Low hardness materials suffer poor stability (±0.1mm fluctuation) and additional finishing processes are required to correct deformation.
4.Material Applicability Limitations
- Too much hardness (such as quenched steel) may cause mold blade breakage, so choose a composite mold structure (such as block mold).
- Ultra-low hardness materials (such as pure aluminum) require anti-adhesion treatment (such as nitrogenation of mold surfaces).
Comparison of stamping process of Different Hardness materials
| Material hardness (HRC) | Typical materials | Stamping process challenge |
Solution
|
Key points of quality control |
| <HRC 20 | Low carbon steel, pure aluminum. | Large rebound and poor dimensional stability. | Increase leveling process or overbending compensation design. | Tolerance ± 0.1mm, no scratches on surface. |
| HRC 20-35 | Stainless steel (1Cr18Ni9Ti). | Mould wear quickly, surface easy to scratch. | Use PVD-coated moulds with lubricating oil to assist stamping. | Ra≤0.8μm, No burrs. |
| HRC 35-50 | Spring steel, tool steel. | Stamping crack risk is high and the ductility reduced. | Multi step progressive stamping+intermediate annealing treatment. | Elongation rate ≥15%, no fractures. |
| >HRC 50 | Titanium alloy, hard alloy. |
The die has a service life of less than 100000 times and is very expensive. |
Diamond coating mold, composite stamping process. |
Dimensional accuracy ±0.02mm requires 3D inspection. |
- Material with high hardness: Priority should be given to alloy molds with slow stamping equipment (velocity ≤50spm) and annealing and softening should be added.
- Low hardness material: Optimize mold clearance (reduce by 5%-10%) and use polyurethane shock absorber to reduce rebound.
- General recommendation: Predicting process risk through material hardness testing (such as Rockwell hardness tester) and test pressure if necessary.
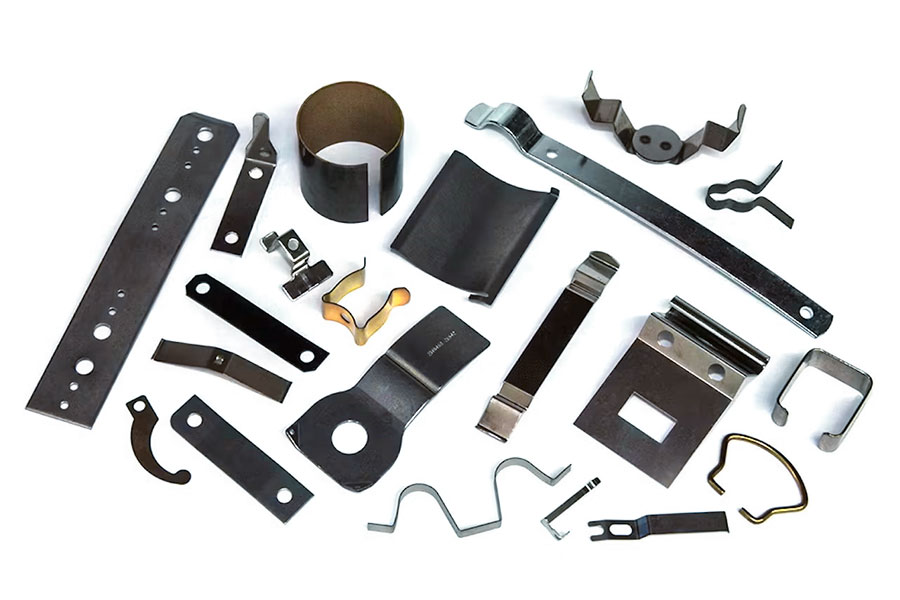

How to reduce the cost of metal stamping?
1.Improving accuracy and reducing waste
High-precision equipment and technology:
- Adopt ±0.005mm ultra precision machining technology (JS core technology) to reduce the scrap rate caused by size deviation and reduce secondary processing cost.
- The CAD/CAM system simulates stamping process, optimizes mold design and parameter setting in advance, and avoids material waste in actual production.
Automated production and intelligent detection: Automatic stamping equipment is combined with real-time quality control system to reduce manual intervention errors and improve yield rates.
2.Material management and selection strategy
Adaptability of a variety of materials: Use JS's metal material database of metal materials (such as stainless steel, aluminum alloy, copper alloy, etc.) to select the most cost-effective materials based on product performance and avoid overdesign.
Residual material recycling and nesting technology: Maximize board utilization (15%-20% increase in JS's material utilization rate) through intelligent typesetting algorithms, reduce corner material waste, and support the recycling of materials such as aluminum and steel.
3.Process efficiency and rapid response
Standardized and modular design: Provides a standardized metal punch library (connectors, casings, etc.) to shorten design lead times, and supports customers to customize quickly to existing templates to reduce development costs.
Agile production mode: Commit to 1-2 weeks of standard delivery time (including complex orders) and reduce additional costs for emergency orders through lean production management and priority scheduling.
4.Collaborative design and process collaboration
Early intervention in client design: The JS team provides pre-design review services to optimize the structural strength, tolerance fit, and assembly feasibility of metal punch to avoid additional costs associated with later modifications.
Mold sharing and lifecycle management: Provide long term maintenance and optimization services for high frequency order molds, extend the lifespan of molds (the average life of JS molds is 30% longer than industry standard), and dilute unit cost of individual products.
5.Sustainable production reduces costs and improves efficiency
Green manufacturing certification: Energy energy consumption has been reduced (JS energy consumption has been reduced by 15%) through the implementation of the ISO 14001 environmental management system and the introduction of energy-efficient stamping equipment and renewable lubricants.
Reduce process and logistics costs: Provide Design stamping surface processing one-stop service (JS integration capability covers the entire chain), eliminating intermediate costs.
How does JS company ensure the accuracy of metal stamping?
Cutting-edge equipment and precision machining technology
1.Ultra precision stamping equipment
- Equipped with a Germany/ Japan imported high-precision servo stamping machines with repeat positioning accuracy ±0.002mm and support tolerance ±0.005mm.
- Adopt ball screws, straight line guide rail and so on transmission systems, reduce mechanical error, guarantee the stability of shape and position tolerances of hardware punch.
2.Mold design and manufacture
- CAD integration software is used to simulate stamping process, optimize mold structure (such as convex die clearance, guidance accuracy), and reduce burrs and deformation risk.
- The mold material is made of SKD11. After heat treatment, the hardness reaches HRC60 or above, and the service life can reach millions of stamping cycles, ensuring consistency of mass production.
Intelligent process control systems
1.Real-time quality monitoring
- Integrated optical measurement system and automation equipment, real-time measurement of punch size, flatness, hole accuracy, automatic clearance of non-conforming products.
- Through statistical process control Analyze production data, dynamic adjustment of stamping parameters (pressure, speed, temperature) to prevent batch deviations.
2.Adjustment of material properties
Match the best material grade (e.g. Al6061) and thickness (0.1-5mm) to the application of metal punch (e.g. automotive sheet metal and electronic components) to avoid rebound or cracking due to insufficient material ductility.
Full-process quality management system
1.ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certification
- Strictly in accordance with industry standards for auto parts, 100% of tests are performed from the time the raw materials are stored to the time the finished product is out of storage, with measurement accuracy of key dimensions reaching μ level (0.001mm).
- Provide production parts approval process documentation, including size reports, material certifications and performance testing data to ensure customer verification safety.
2.Reverse engineering and rapid feedback
For accuracy of customer feedback, the failure analysis is carried out using coordinate measuring machine, and the improvement scheme is provided within 48 hours to shorten the debugging cycle.
Summary
Metal stamping is the core technology of modern industry, which can effectively transform metal sheets into high-precision metallic stamps. Process flow includes design optimization, material adaptation, mold manufacturing, stamping production and reprocessing, each step requiring strict tolerance and deformation control. The hardness of the material directly influences the wear and tear of the die, the selection of process adjustment parameters and the quality of the finished product.
With ultra-precision its ultra precision stamping equipment mold technology full process quality management system JS Company ensures that metal stamping tolerance is controlled to ±0.005mm and material utilization is increased to over 92%. At the same time, it reduces energy consumption and waste through sustainable manufacturing practices. Providing efficient, reliable and cost-effective solutions for manufacturing highlights the irreplaceable role of metal stamping in precision manufacturing.
Disclaimer
The content of this page is for informational purposes only.JS SeriesNo representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, are made as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that the performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features,material quality and type or workmanship that the third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide through the jusheng network. This is the responsibility of the buyerAsk for a quote for partsto determine the specific requirements for these parts.please Contact us Learn more information.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. With over 20 years of experience serving more than 5,000 customers,we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal fabrication,3D printing,Injection molding,metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with more than 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers and is ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it's low-volume production or mass customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyIt means choosing efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, please visit our website:jsrpm.com
FAQs
1.What tools are needed for metal stamping?
Includes high-precision die, press, tool, lubricant, clamping devices, quality inspection equipment, etc. Mould ensures accuracy of shape, press provides punch pressure, tool completes cutting, lubricant reduces friction, fixture fixed plate, test equipment ensures consistency of dimensions.
2.What materials are suitable for stamping?
Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, copper, steel plates, etc. Thickness (0.1-5mm) and strength shall be selected according to the purpose of the product, taking into account ductility, corrosion resistance and cost requirements.
3.Do stamped parts need additional processing?
Stamped parts usually require burr removal, polishing, or surface treatment to improve appearance, rust resistance, or functional compatibility. Treatment depends on the product's purpose, for example, electronic components require high-precision polishing and automotive parts often require anticorrosive coatings.
4.What are the consequences of stamping metal too fast?
High speed stamping may cause material tearing or mold impact damage due to inertia. Normally, stainless steel stamping speed is controlled at 50-80 times perminute, while aluminum can be ramped up to 120 times perminute, depending on the malleability of the material.